Describe the Relationship Between Ocean Acidity and Ocean Ph
Permalink to Description. When carbon dioxide is absorbed by the ocean it dissolves to form carbonic acid.

The State Of Ocean Acidification Ecos
The importance of coastal resources goes beyond food to a potential loss of cultural heritage.
. This indicator describes changes in the chemistry of the ocean that relate to the amount of carbon dioxide dissolved in the water. The harmful impact of ocean and coastal acidification on marine life especially shellfish may affect the livelihood of vulnerable indigenous communities in Alaska on the West Coast and the Gulf Coast that depend on these coastal resources. Ocean acidification is a term used to describe the changes in the chemistry of the worlds seas primarily as a result of burning fossil fuels.
Future predictions indicate that the oceans will continue to absorb carbon. Ocean acidification is an often overlooked consequence of humankinds release of carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere from fossil fuel burning. The distribution of DIC between these species varies with seawater pH Figure 2.
The pH of oceans is inversely proportional to the concentration of carbon dioxide in the water. In the high-emissions scenario global average ocean pH levels would fall to around 767 by 2100 roughly five times the amount of acidification that has already occurred. But this is changing sea surface chemistry dramatically.
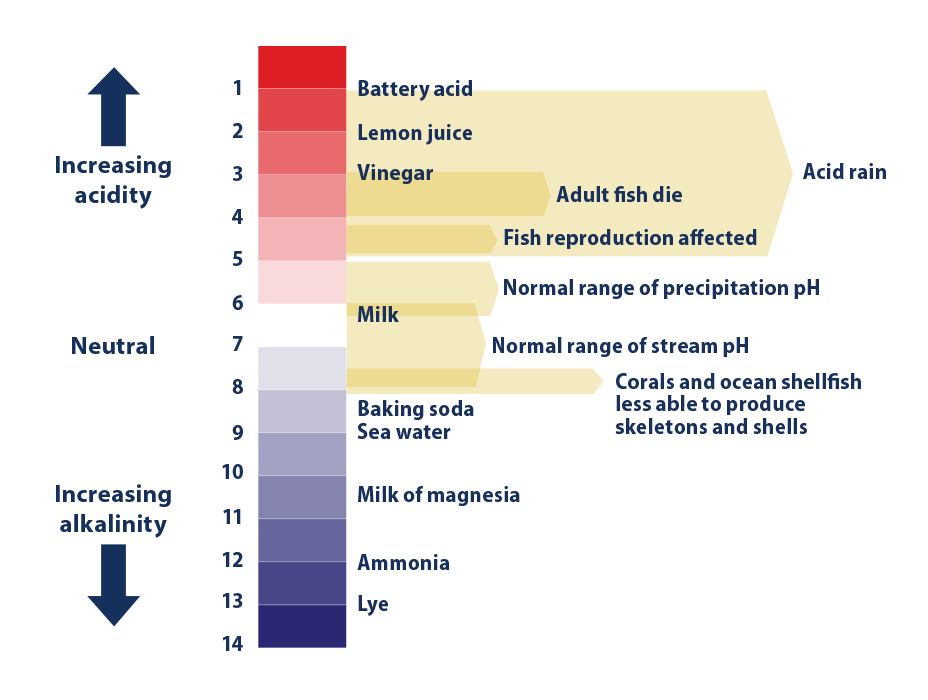
The impact of ocean acidification on corals is one of these dangers. Watch our video for a quick overview. Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution the pH of surface ocean waters has fallen by 01 pH units.
The result not surprisingly is that the ocean becomes more. Our oceans are an incredible carbon sink they absorb about 25 percent of the carbon dioxide humans produce every year. Thus making the ocean more acidic.
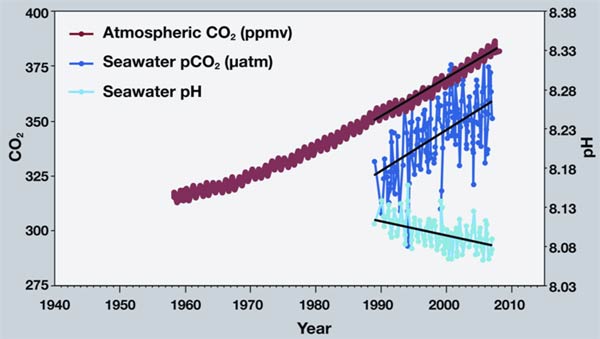
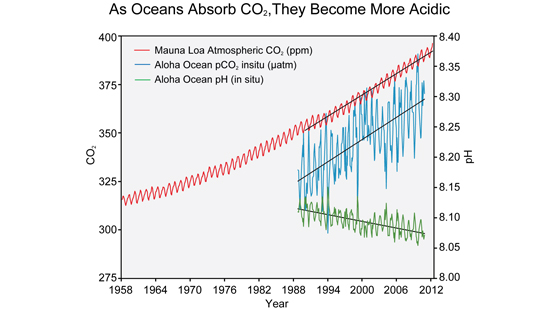
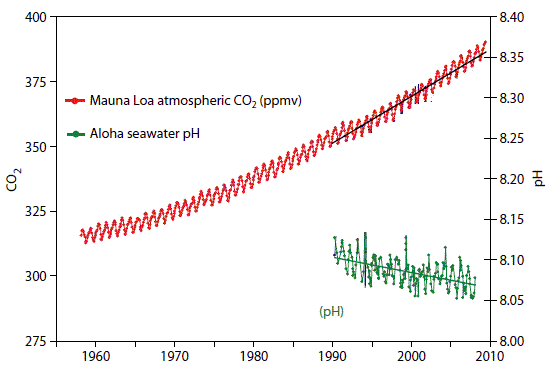
As you watch the interactive click forward note that each data set shows considerable variability in yearly measurements but when this variability is averaged over time definite trends can be observed. Availability and increased acidity. So exactly what is ocean acidification.
Ocean acidification refers to a reduction in the pH of the ocean over an extended period of time caused primarily by uptake of carbon dioxide CO 2 from the atmosphere. Typically the surface waters of todays ocean have a pH of around 81 meaning that HCO 3- is the dominant. Oceans absorb carbon dioxide CO 2 from the atmosphere.
Oceanographers and marine biologists are now seeing a relationship between changes in ocean pH and carbon dioxide dissolved in sea water. Such large changes in ocean pH have probably not been experienced on the planet for the past 21 million years and scientists are unsure whether and how quickly ocean life. As a consequence of acidification marine life face a two-fold challenge.
17 1 The carbon dioxide system in seawater. The main cause of ocean acidification is humans burning of fossil fuelsAs the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by the ocean also increases. Marine scientists are concerned that changes to the oceans pH levels will have severe consequences for marine wildlife and ecosystems.
Ocean Acidification Overview Lesson 3 describes the ocean as a carbon sink that absorbs atmospheric carbon. This research investigation sought to identify the relationship between the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide and pH levels in oceans. For more than 200 years or since the industrial revolution the concentration of carbon dioxide CO 2 in the atmosphere has.
Dickson Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California USA 11 Introduction The worlds oceans can be thought of as a dilute solution of. Since the pH scale like the Richter scale is logarithmic this change represents approximately a 30 percent increase in acidity see our pH primer web page for more information. Excess carbon dioxide enters the ocean and reacts with water to form carbonic acid which decreases ocean pH ie makes seawater less basic and lowers carbonate ion concentrations.
The evidence suggest a correlation between atmospheric carbon dioxide and decrease of pH levels as the concentration of C O 2. Increases the pH decreases. Climate Change Indicators.
What is ocean acidification. Equilibrium chemistry and measurements Andrew G. Ocean acidity refers to the concentration of hydrogen ions in ocean seawater regardless of ocean pH which is fundamentally basic eg pH 7.
Acidity is a measure in units of pH of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution in this case ocean water. In the activity students develop and test a hypothesis about how acidic. Ocean Carbon Dioxide Levels and Acidity 19832018.
Although the chemistry of this effect is well understood and not much debated the full consequences of ocean acidification for marine ecosystems and human well-being are only. Ocean surface waters have become 30 more acidic over the last 150 years as they have absorbed large amounts of CO 2 from the atmosphere 66 and anthropogenically sourced CO 2 is gradually invading into oceanic deep waters. Ocean acidification refers to a reduction in the pH of the ocean over an extended period of time caused primarily by uptake of carbon dioxide CO2 from the atmosphere.
Ocean acidity as measured by pH has increased by 30 since the industrial revolution and scientists predict pH will continue to change as increasing amounts of carbon dioxide are absorbed by oceans. Students read evidence that increasing carbon dioxide CO 2 levels in the ocean are correlated with decreasing ocean pH. In other words the higher the carbon dioxide the lower the pH and the ocean becomes more acidic.
This figure shows the relationship between changes in ocean carbon dioxide levels measured in the left column as a partial. A lower pH data indicates the ocean is becoming more acidic whereas a higher pH indicates the ocean water is becoming less acidic. Due to increases in carbon emissions more CO 2 is entering the worlds oceans which creates additional carbonic acid in the water.
Laboratory studies suggest changing ocean chemistry will 1 harm life forms that rely on carbonate-based shells and skeletons 2 harm organisms sensitive to acidity and 3 harm organisms higher up the food chain. Ocean acidification is the ongoing decrease in the pH value of the Earths oceans caused by the uptake of carbon dioxide CO 2 from the atmosphere. Ocean acidification which occurs when CO2 in the atmosphere reacts with water to create carbonic acid has already increased ocean acidity by 30 percent Doney 2006.
Carbon dioxide reacts with seawater to form carbonic acid. For millions of years the exchange of CO 2 between the surface of the ocean and the atmosphere remained constant.
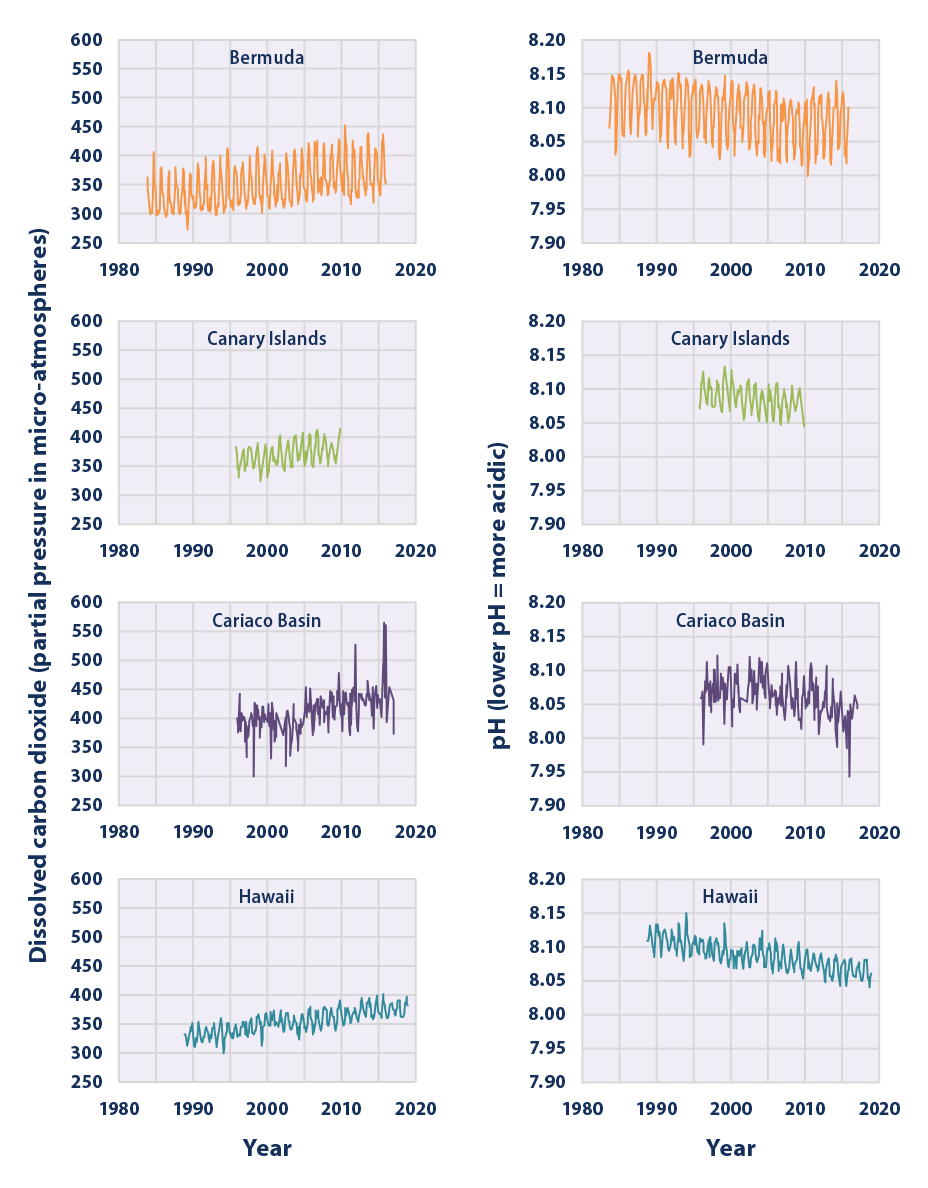
Climate Change Indicators Ocean Acidity Us Epa

Ocean Acidification How Carbon Dioxide Is Hurting The Seas Britannica
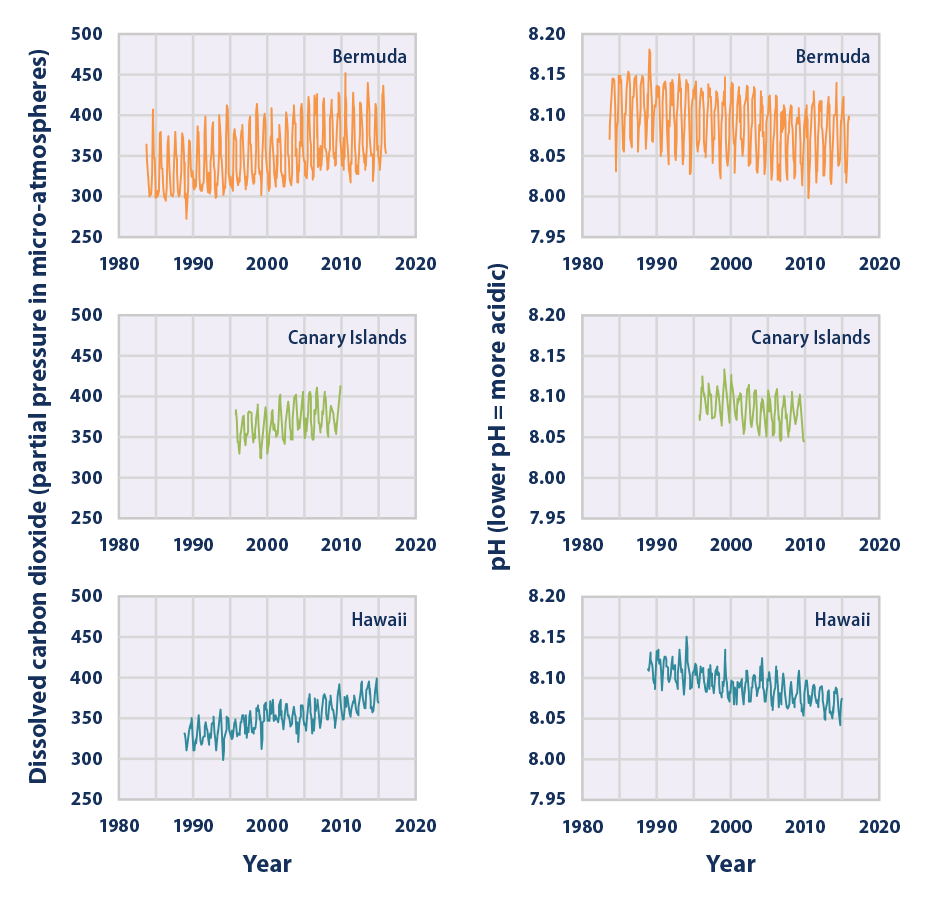
Climate Change Indicators Ocean Acidity Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa
Un Atlas Of The Oceans Subtopic
Is Ocean Acidification A Threat Energy Matters
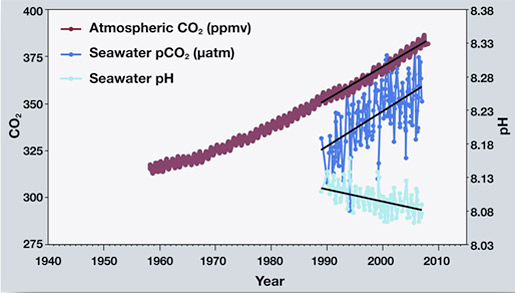
What Is Ocean Acidification Alaska Ocean Observing System
Ocean Acidity Over The Past 25 Million Years And Projected To 2100 European Environment Agency
Ocean Acidification European Environment Agency

Acidification Conservation In A Changing Climate
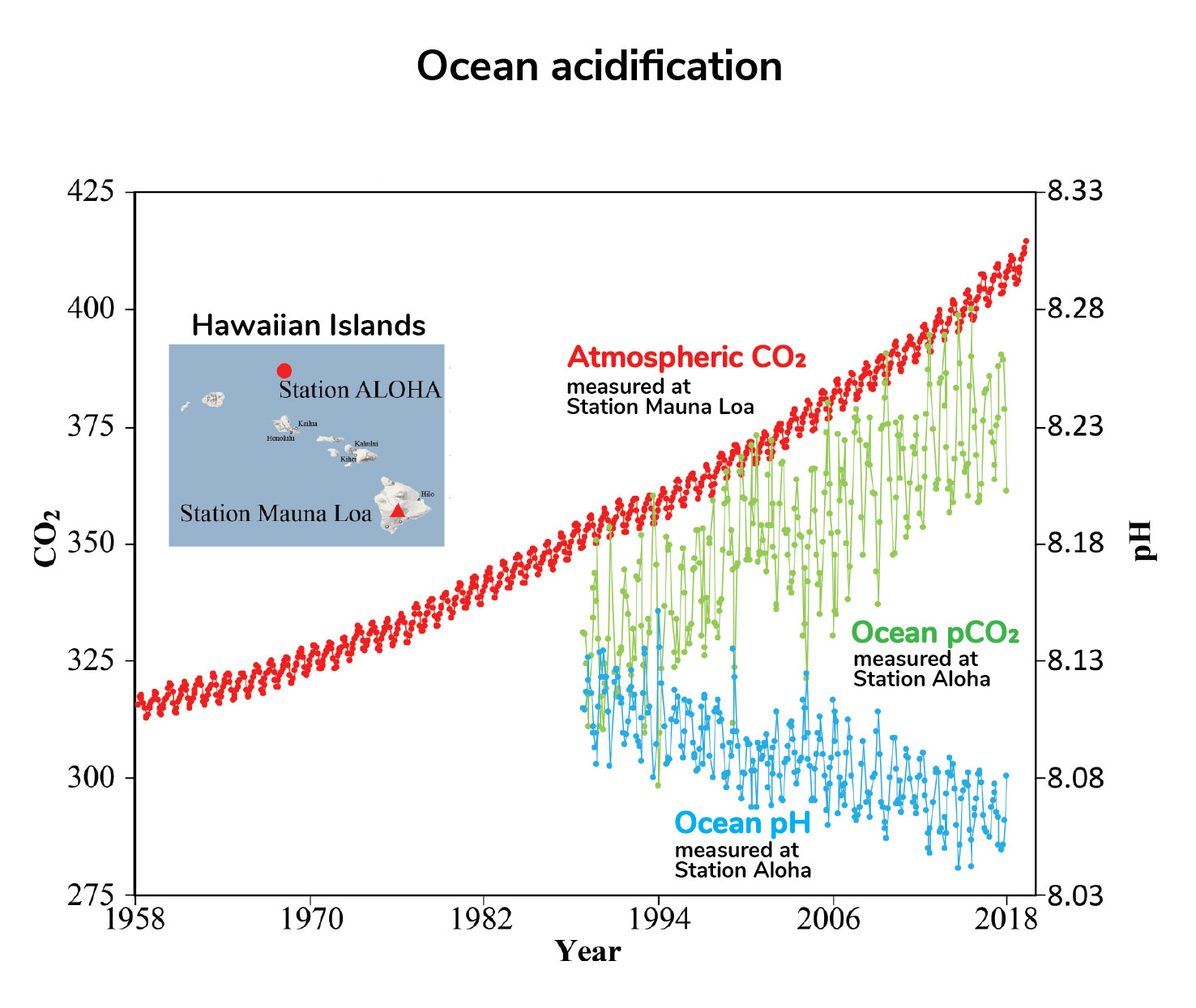
Ocean Acidification Understanding Global Change
How Will Ocean Acidification Affect Ocean Sound Levels Discovery Of Sound In The Sea
Oceans On Acid Sailors For The Sea

Learn About 5 Scary Consequences To Ocean Acidification Dolphinaris


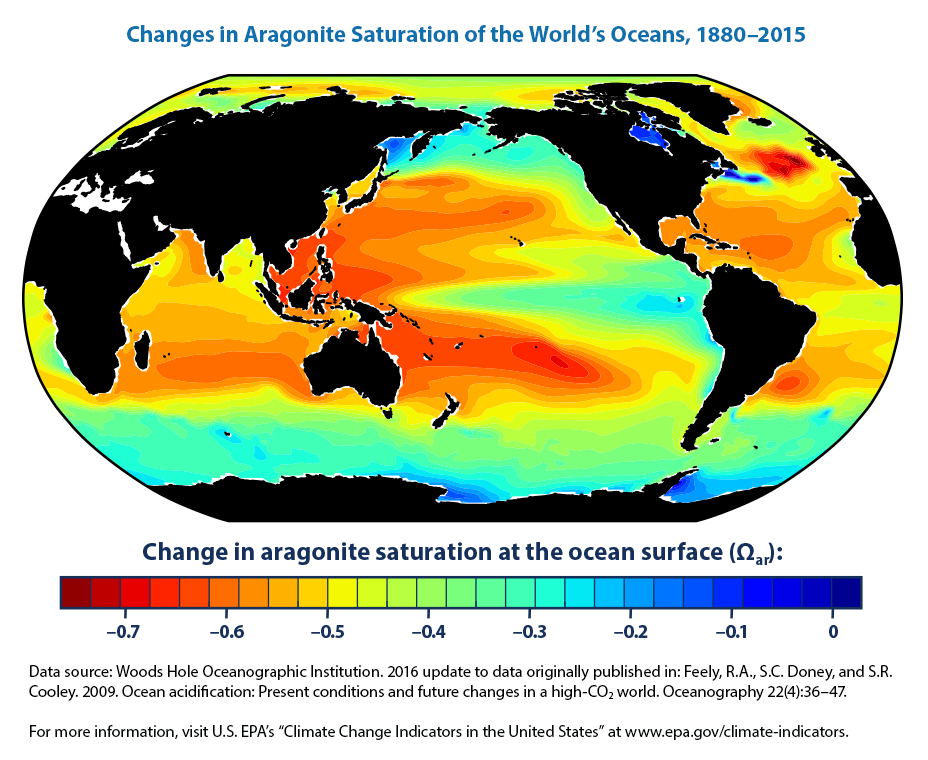
Comments
Post a Comment